| An object in motion is said
to have velocity or acceleration. While we are all
used to the word "speed," this word does not truly
quantify any useful measurements in science since it is
a measure of scale.
Velocity is the preferred
measure of "speed" when dealing with anything
scientific as it can be quantified based on distance
traveled. This is presented by some number over
distance traveled - like 70 km/h. This formula
demonstrates how velocity is determined:
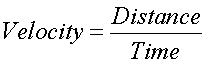
or:
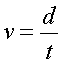
Acceleration is another one of those tricky words.
We are familiar with the accelerator pedal (gas
pedal) on a car, and rightly defined as detonating
additional gas and air produces more combustion
resulting in a faster turning engine. However, this
is only half of the story.
Acceleration is defined as any change in vector.
This means that a car that speeds up, slows down,
turns left and turns right is undergoing
acceleration. We have already seen velocity:
distance traveled in a particular time frame. This
is taking into account a constant speed. In order to
determine acceleration, we need to document any
changes in velocity over time:
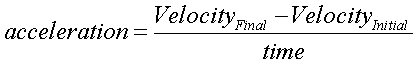
or:
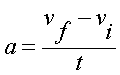
To add to some confusion, it is possible to have
negative acceleration. An example would be a car
traveling in reverse. A car slowing down is also
negative acceleration due to opposing forces.
Back to Top
|

